A computer is a programmable device that accepts data as input and process it with a set of instructions and produces the result as output.
A computer consists of the following four parts,
- Input Unit.
- Output Unit.
- Memory Unit.
- Central Processing Unit.
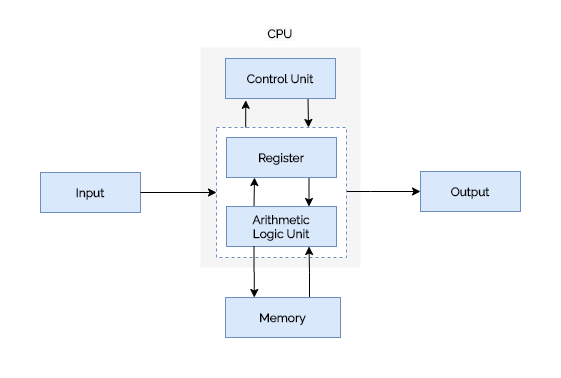
Input Unit
- The input unit accepts data and instructions from user.
- Digitise received data.
- Supply digitised data to computer system for processing.
Output Unit
- Accept processed data from computer.
- Convert binary data to humanely acceptable form.
- Supply this result to user.
Memory
- Store data to be processed by the system.
- Store Intermediate result.
- Store final result.
Central Processing Unit
- The CPU retrieves and executes all the instructions of a computer program.
- It consist of
- Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU).
- Control Unit.
- Registers.
Arithmetic Logic Unit
- The ALU performs all arithmetic and logical operations.
Registers
- These are the temporary storage location within the CPU.
- The CPU uses several types of registers for specific functions.
- Eg: Accumulator, PC, IR, etc.
Control Unit
- The control unit controls and coordinates entire computer system.
- Fetches instruction from memory.
- Decodes the instruction.
- Execute the instruction.
- Control data transfer between memory and I/O devices.
Buses
- Common communication path.
- Physical group of signal lines that have a related function.
- Allows transfer of electrical signals between different components.
- Most used bus architecture is the three bus architecture. (Data bus, Address bus, Control bus)
