World Wide Web
A networked system of public web pages that can be accessed via the Internet is called the World Wide Web(WWW or W3).
World Wide Web Consortium
W3C or World Wide Web Consortium is an international community that develops web standards. The primary motive of W3C is to develop protocols and guidelines that will ensure the growth of the World Wide Web. They guide the Web to its full potential.
Web Browser
A web browser is a software that allows people to access websites. Chrome, Firefox, Internet Explorer and Safari are some popular examples. To visit a website, you have to type its web address into the address.
Web Server and Web Hosting
When you ask the browser for a webpage, it sends a request across the world wide web to a special computer known as a web server. Web servers are dedicated computers that are always connected to the Internet. The websites we see on the internet is hosted by web servers.
Some large companies run their webserver. However, using the services of a web hosting company, which will charge you a fee to host your site, is more convenient.
URL
The address given to a web page or any other resource on the web is called URL (Uniform Resource Locator). URLs are managed by web servers. A URL is made up of several parts, some of which are required and others of which are optional. The URL below highlights the most important parts.
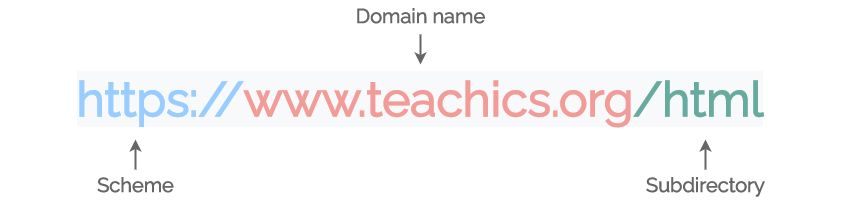
When a web server accesses a page on your website, the scheme tells it which protocol to use. SOme standard protocols are http://, https://, ftp://, mailto://, etc.
The domain name specifies which web server is being requested. It consists of the name of your website name and a top-level domain such as .com, .org, .edu, etc.
The subdirectory or file path tells which particular section or resource of the web page they are on.
DNS
The Domain Name System is a network of servers that maps the URL of a webpage to the IP address of the webserver where the website is located. When a user types a URL into a browser, a DNS query is made and the IP address associated with that domain name is returned. This IP address allows the browser to reach the webserver where the requested web page is hosted. The Browser, DNS, and Web server communication are represented in the following figure.

HTML
HTML is a computer language that was created primarily for the creation of websites. It is easy to learn, but it is effective and powerful. HTML is an abbreviation for HyperText Markup Language. HTML 5 is the new specification of HTML that is specifically designed for the World Wide Web.
HTML is a markup language. The markup instructions included within a webpage describe the structure of the document to the browser software. So, an HTML page is essentially a text file that contains the information you want to publish as well as the relevant markup instructions indicating how the browser should structure or present the document.
HTML Document Structure
See the following HTML code. Don’t be concerned about the meaning of the code yet. We’ll take a closer look at it in the following tutorials. For better understanding, HTML code is written in red color and the text we see on the screen is given in black.

Markup elements are composed of a start tag, such as <p>, and typically, but not always, an end tag which is denoted by a slash within the tag, such as </p>. Some markup elements which does not include any content need no close tag at all.
The tag pairs <html>, <head> and <body> are used to specify the overall structure of the document.
The title of the document usually appears in the title bar of the Web browser is specified using the <title> tag pair.
DOCTYPE or DTD
The <!DOCTYPE> statement indicates which version of HTML is used in the document. It is not an HTML tag. In HTML 5, the declaration takes the following form,
<!DOCTYPE html>
In older versions of HTML, the declaration must refer to a DTD. DTD is a document that defines a formal standard of HTML that can be read by machines.
For example, HTML 4.01 use the following form of declaration,
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
