In c programming, multidimensional arrays can be simply defined as arrays of arrays. Multidimensional arrays store data in tabular form.
Declaring Multidimensional Arrays in C
The declaration of an n-dimensional array takes the following form,
dataType arrayName[size1][size2] ... [sizeN];
For example,
int A[3][5];
Here A is a 2-dimensional array with 3 rows and 5 columns. The total number of elements that can be stored in a multidimensional array is the product of the size of all the dimensions. The size of this two-dimensional array will be 15.
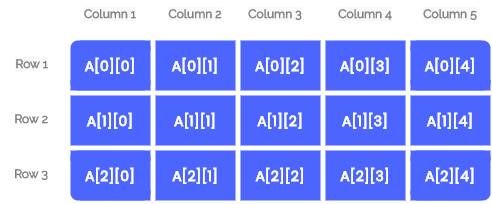
Elements in this array can be referred to by A[i][j] where i is the row number and j is the column number.
A simple example of a 2-dimensional array having 3 rows and 5 columns is given below.

Here A[0][0] = 5, A[0][1] = 3, A[0][2] = 10, A[0][3] = 8 and A[0][4]=15.
Similarly, A[1][0] = 11, A[1][1] = 19, A[1][2] = 7, A[1][3] = 1, A[1][4] = 4 and so on.
Initializing Multidimensional Arrays
A 2-dimensional array can be initialized in any of the following ways:
int A[3][5] = { {5, 3, 10, 8, 15}, {11, 19, 7, 1, 4}, {8, 9, 2, 3, 5} };
int A[][3] = { {5, 3, 10, 8, 15}, {11, 19, 7, 1, 4}, {8, 9, 2, 3, 5} };
int A[2][3] = {5, 3, 10, 8, 15, 11, 19, 7, 1, 4, 8, 9, 2, 3, 5};
It will create an array of the following form:

A 3-dimensional array can be initialized in a similar way. For example
int A[3][2][4] = {
{{1,7,8,2},{5,6,1,0}},
{{5,3,0,2},{4,6,1,8}},
{{8,6,2,1},{8,4,0,3}}};
Example: Sum of two matrices
// finding the sum of two matrices of order 3*2
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a[3][2], b[3][2], sum[3][2];
// Getting elements of 1st matrix
printf("Enter elements of 1st matrix\n");
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < 2; ++j)
{
printf("Enter a%d%d: ", i + 1, j + 1);
scanf("%d", &a[i][j]);
}
// Getting elements of 2nd matrix
printf("Enter elements of 2nd matrix\n");
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < 2; ++j)
{
printf("Enter b%d%d: ", i + 1, j + 1);
scanf("%d", &b[i][j]);
}
// finding sum
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < 2; ++j)
{
sum[i][j] = a[i][j] + b[i][j];
}
// Displaying the resultant matrix
printf("\nSum Of Matrix\n");
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 2; ++j)
{
printf("%d\t", sum[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
Output
Enter elements of 1st matrix Enter a11: 1 Enter a12: 6 Enter a21: 2 Enter a22: 8 Enter a31: 0 Enter a32: 3 Enter elements of 2nd matrix Enter b11: -3 Enter b12: 5 Enter b21: 9 Enter b22: 0 Enter b31: 2 Enter b32: 3 Sum Of Matrix -2 11 11 8 2 6

give simple example for multidimensional array
Added.